Glucosamine, with or without chondroitin, is a popular and high selling neutraceutical with claims to improve symptoms associated with painful osteoarthritis (OA). Clinical trials testing purported benefits have yielded mixed results, with manufacturer sponsored trials showing benefits while most unbiased studies have generally not shown benefit over placebo. Previously, in a large clinical trial of glucosamine hydrocholoride with or without chondroitin sulfate, neither agent demonstrated efficacy over placebo in treating pain in individuals with knee OA.
Arthritis News
FDA Arthritis Drug Advisory Committee Recommends Approval of Febuxostat for Treatment of Hyperuricemia of Gout

At their November 24, 2008 meeting, the FDA Arthritis Drug Advisory Committee heard updated efficacy and safety data for febuxostat for the treatment of gout-associated hyperuricemia. The committee’s recommendation was carried on a vote of 12 to 0. Final FDA approval of the drug is pending; however, FDA approval generally follows the recommendations of the advisory committee.
Postmenopausal Hormone Replacement May Reduce Uric Acid Levels in Women
Elevated uric acid levels and the incidence of clinical gout are exceedingly rare in women before menopause but rise after cessation of menses, potentially explained by an effect of estrogen on the renal handling of uric acid. Despite this well established association, little is known about the effect of post-menopausal estrogen replacement on uric acid levels in women.
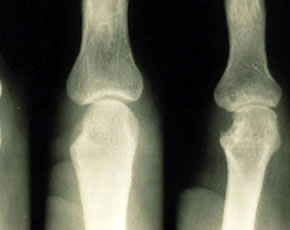
Safety and Efficacy of Repeated Doses of Pegloticase for Gout Studied
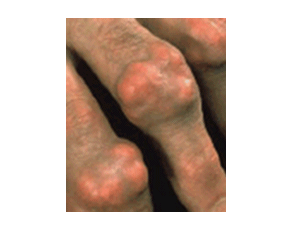
Chronic tophaceous gout remains difficult to treat with available medications. Replacement of uricase, an enzyme essential for uric acid metabolism yet functionally deficient in humans, represents a promising therapy for uric acid lowering and resolution of tophi. Rasburicase, an available recombinant form of uricase, is limited in its use for gout due to immunogenicity.
PAD-4 Autoantibodies Identified as a Novel Severity Factor in RA
Antibodies against citrullinated proteins have emerged as powerful diagnostic and prognostic tools in RA that may contribute to the initiation phases of the disease. The enzymes that catalyze the citrullination process, known as peptidyl argenine deiminases (or PADs), may also be involved in the initiation and propagation steps of the RA disease process. Additionally, autoimmunity to these catalysts may identify a subset of RA patients with unique disease phenotypes.