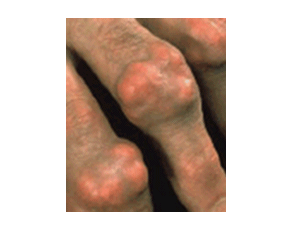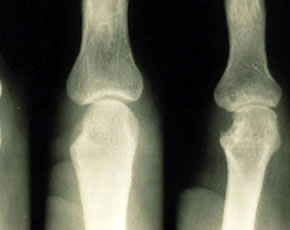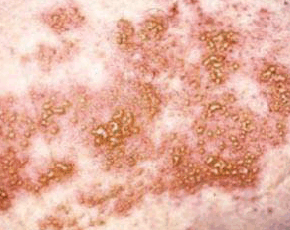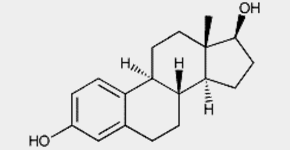
Elevated uric acid levels and the incidence of clinical gout are exceedingly rare in women before menopause but rise after cessation of menses, potentially explained by an effect of estrogen on the renal handling of uric acid. Despite this well established association, little is known about the effect of post-menopausal estrogen replacement on uric acid levels in women.